Measuring the Turns Ratio of Transformers
The Key to Quality Control
Transformers are essential components in power systems and signal transmission. Utilizing the principle of electromagnetic induction, they transfer electrical energy or signals from one circuit to another. Composed of a primary coil, a secondary coil, and a magnetic core, transformers are primarily used to alter alternating current (AC) voltage, current, and impedance. Among these, the turns ratio between the primary and secondary coils is an exceedingly important parameter affecting the transformer's overall performance and safety.

Importance of the Turns Ratio
The turns ratio between the primary and secondary coils not only reflects the effective voltage ratio between the primary and secondary circuits but also inversely correlates with their effective current values when no-load current can be disregarded. In simpler terms, the proportion of current or voltage between both sides of the transformer depends on the number of turns in each coil. The side with more turns will have a higher voltage but a lower current.
Why Measuring the Turns Ratio is Essential
▼Spec Consistency
On the production line, each transformer must meet predetermined specifications. Accurate measurement of the turns ratio ensures this, helping to maintain high quality standards.
▼Performance Assurance
An incorrect turns ratio can lead to unstable operation of the transformer and may even damage equipment connected to it.
▼Safety
An incorrect turns ratio could result in either too high or too low output voltages, posing significant safety risks to both personnel and equipment.
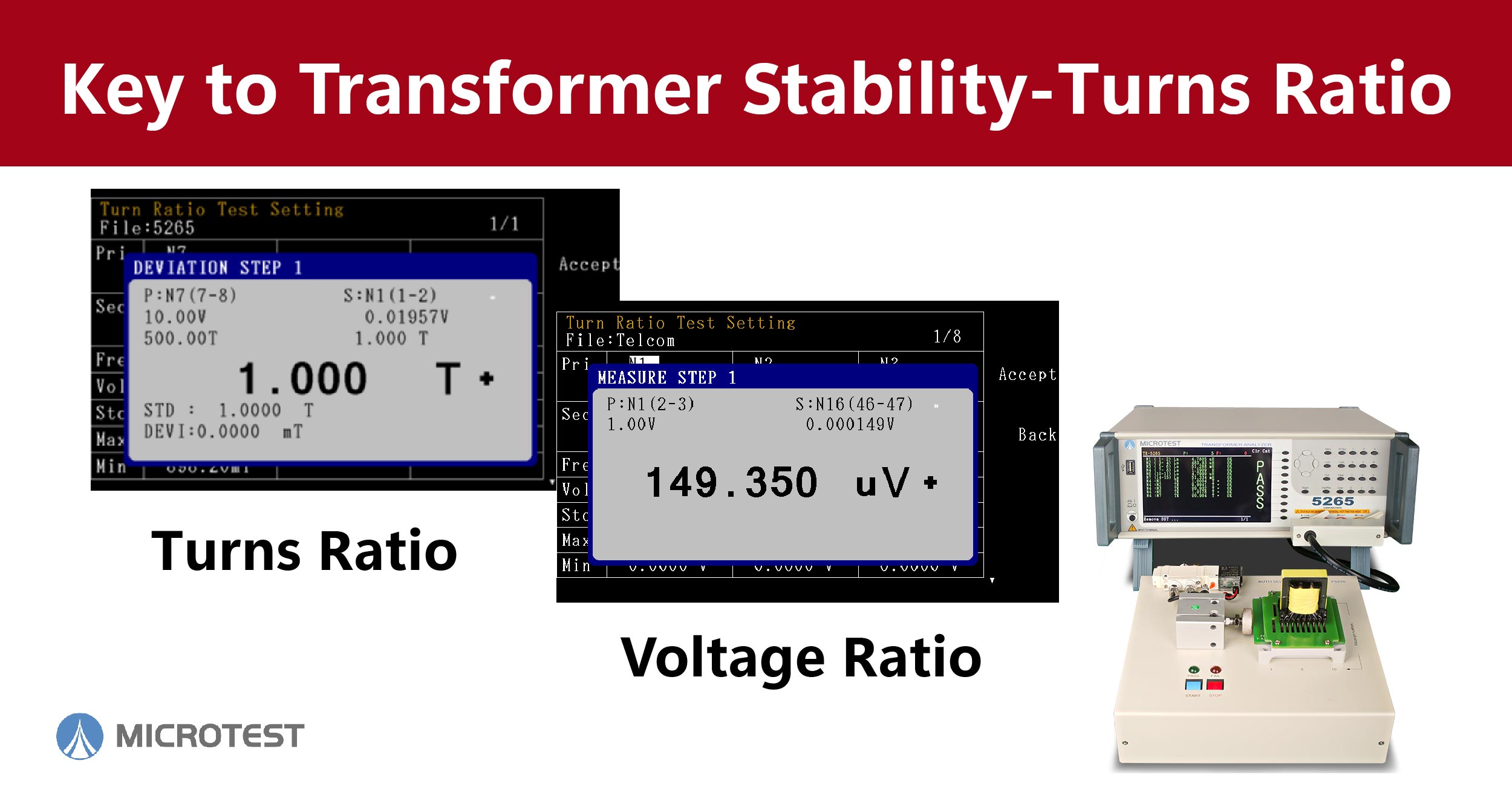
MICROTEST 5260 Series: Different Methods for Measuring Turns Ratio in Transformers
●TR (Turns Ratio Voltage Method)
The Turns Ratio Voltage Method (TR) involves applying an alternating current (AC) voltage to the primary coil and measuring the AC voltage in the secondary coil. The objective is to verify whether the turns ratio and phase between the coils are correct. One of the advantages of this method is that the measurement results include the turns ratio that accounts for losses. The measured ratio will be higher than the actual turns ratio but can reflect the voltage values that research engineers aim to achieve.
●TRL (Turns Ratio Inductance Method)
The Turns Ratio Inductance Method (TRL) involves measuring the inductance values of each coil. The turns ratio is then calculated based on these inductance values. This method is more accurate for transformers with higher leakage inductance. It avoids the influence of transformer losses, resulting in a turns ratio measurement that is closer to the actual physical transformer. The drawback is that when dealing with high leakage inductance, the actual voltage ratio can be significantly affected.
Transformer Tester 5265 Spec




