- Products
- Solution
- Support
- About
- Contact Us
-

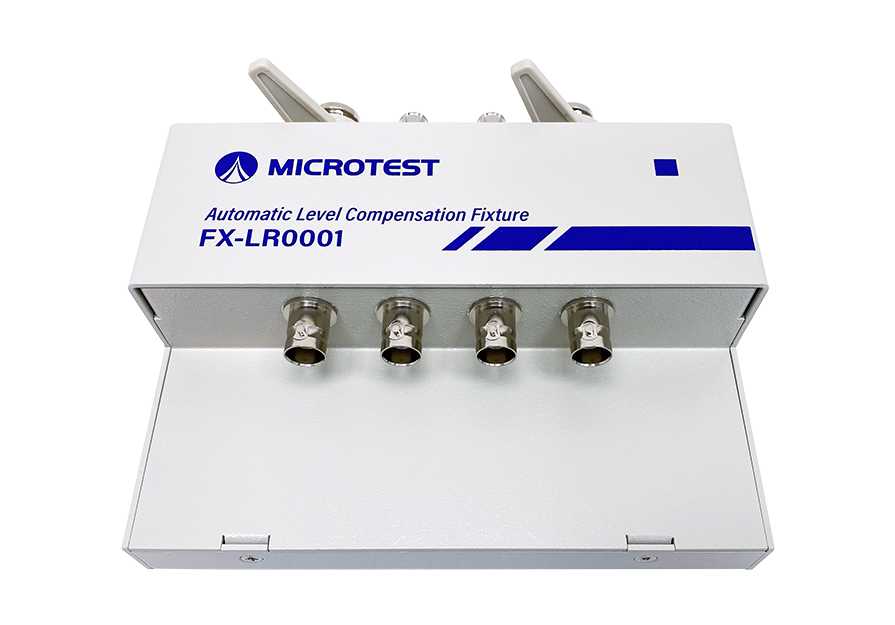
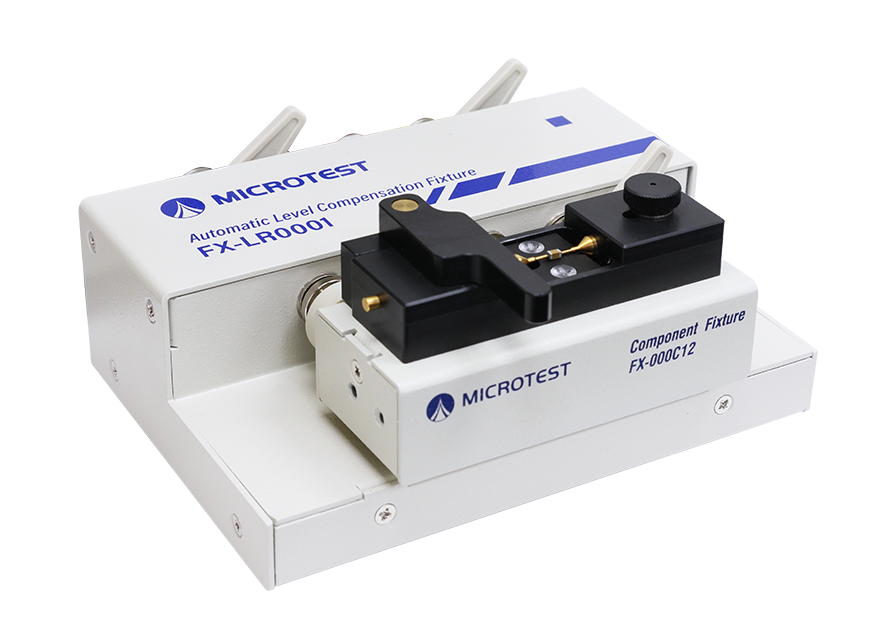
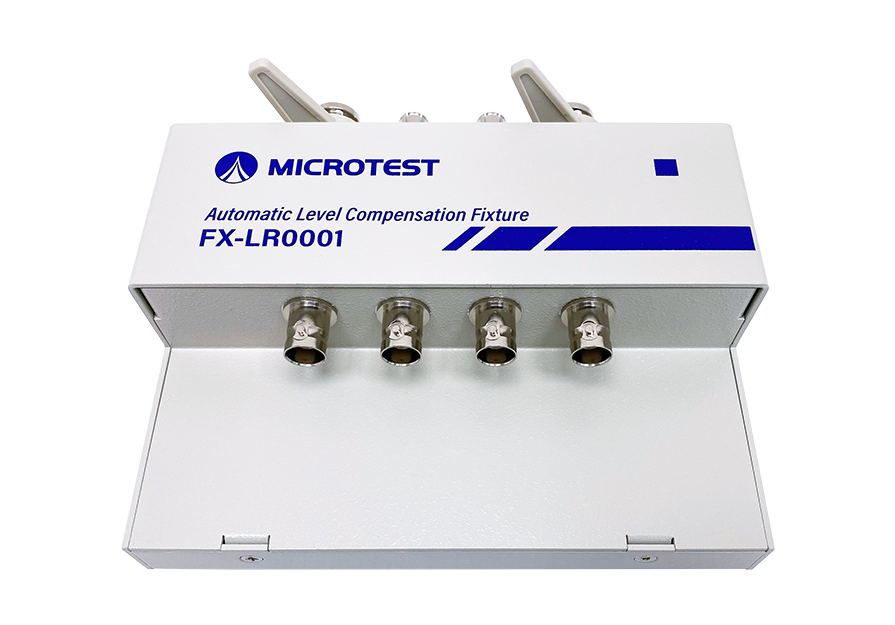
Products
Search
14F-6, No. 79, Sec. 1, Xintai 5th Rd, Xizhi Dist., New Taipei City, 22101 Taiwan (R.O.C.)
Tel: 886-2-2698-3877
Fax: 886-2-2698-4089
email : sales@microtest.com.tw